KDDI Corporation (headquartered in Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo; Koji Tanaka, President; hereinafter "KDDI"), KDDI R&D Laboratories, Inc. (headquartered in Fujimino City, Saitama Prefecture; Yasuyuki Nakajima, President; hereinafter "KDDI R&D Laboratories") and Couger Inc. (headquartered in Shibuya-ku, Tokyo; Atsushi Ishii, CEO; hereinafter referred to as "Couger") will launch Japan's first demonstration experiment of "Smart Contracts" utilizing Enterprise Ethereum (Note 1) on September 27, 2017.
KDDI also joined the Enterprise Ethereum Alliance ("EEA") (Note 2) on the same day.
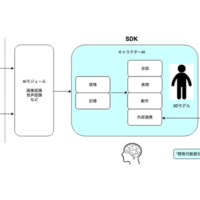
"Smart Contracts" are a mechanism that uses blockchain (Note 3) technology to program promises and contracts that have been exchanged in advance in a form that is difficult to tamper with, and automatically executes them when the conditions are met.
As a first step, KDDI, KDDI R&D Laboratories, and Couger will jointly verify the potential for real-time information sharing and operational efficiency in the process from application to completion of in-store repair of cell phones, utilizing blockchain technology.
In addition, we will verify the possibility of using "Smart Contracts" to link systems between different businesses, such as reuse services, which is a separate business from the repair business. Specifically, we will verify whether the program can automatically identify information between different systems, such as repair price, model change price, and used market price, and make the most appropriate contract when repairing cell phones.
In addition, KDDI and Couger will conduct multiple demonstrations combining IoT, AI, and other technologies with "Smart Contracts" with the goal of providing new experience value that is closer to customers, not limited to experiments in the repair business.
In addition to Couger, which will promote the development of AI, robotics, and blockchain applications, KDDI will work with blockchain developer Trident Arts Corporation, legal tech company Centaurus Works, Inc. and EEA's subscribing members to consider the development of next-generation service infrastructure.
(Note 1) Platform for enterprise distributed applications.
(Note 2) An alliance to share cases, develop standards, and open source programs for Enterprise Ethereum technology. More than 150 companies are participating.
(Note 3) A mechanism that operates constantly and makes it difficult to tamper with data by having multiple computers perform decentralized consensus building. It enables multiple participants on the network to securely share data without the presence of a central administrator.
(Note 4) An application platform that enables the construction and execution of decentralized applications (DApps) and "smart contracts" that operate automatically on the blockchain without the existence of a central management system.